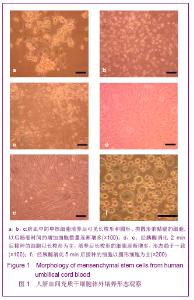
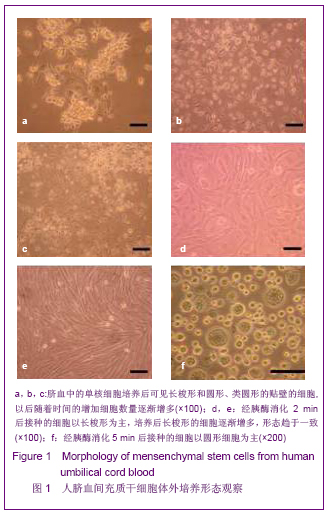
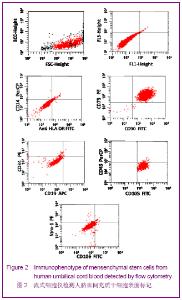
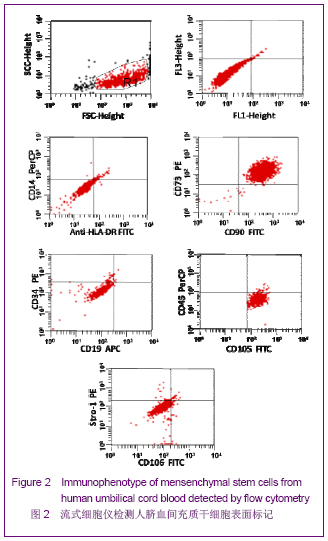
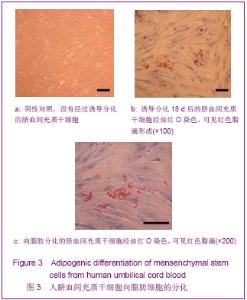
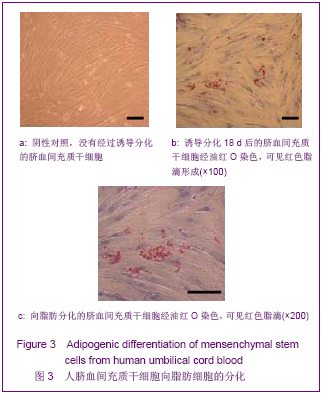
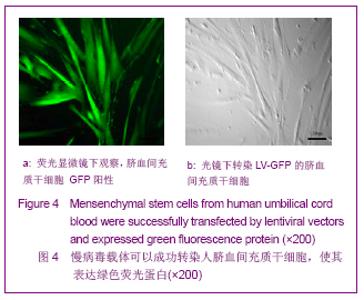
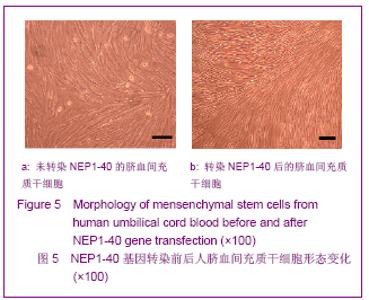
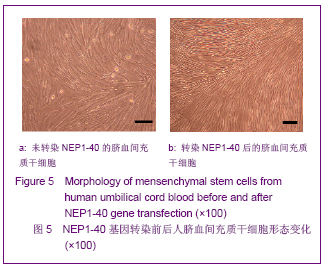
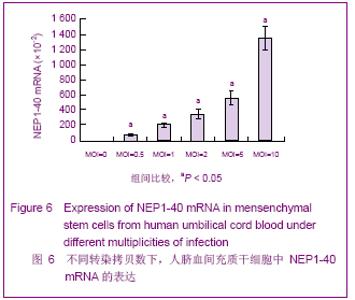
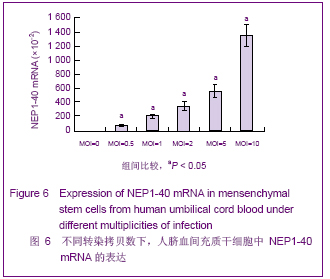
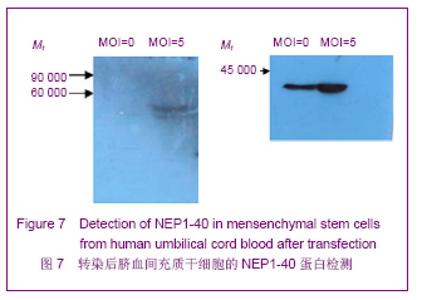
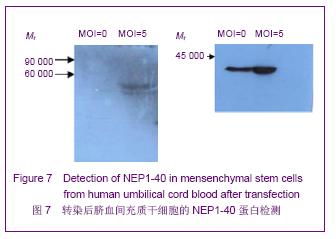
| [1] Brittis PA, Flanagan JG. Nogo domains and a Nogo receptor: implications for axon regeneration. Neuron. 2001; 30(1):11-14.[2] Chen MS, Huber AB, van der haar ME, et al. Nogo-A is a myelin-Associated neurite outgrowth inhibitor and an antigen for monoclonal antibody IN-1. Nature. 2000;403(6768):434-439. [3] McGee AW, Strittmatter SM. The Nogo-66 receptor: focusing myelin inhibition of axon regeneration. Trends Neurosci. 2003; 26(4):193-198.[4] Skaper SD. Neuronal growth-promoting and inhibitory cues in neuroprotection and neuroregeneration. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1053:376-385.[5] Fournier AE, GrandPre T, Strittmatter SM. Identification of a receptor mediating Nogo-66 inhibition of axonal regeneration. Nature. 2001;409(6818):341-346.[6] GrandPréT, Li S, Strittmatter SM. Nogo-66 receptor antagonist peptide promotes axonal regeneration. Nature. 2002;417(6888):547-551.[7] Li S, Strittmatter SM. Delayed systemic Nogo-66 receptor antago-nist promotes recovery from spinal cord injury. J Neurosci. 2003;23(10):4219-4227.[8] Wang SY, Ren P, Xie S, et al. Shengwu Gongcheng Xuebao. 2008;24(2):2061-2067.王淑艳,任萍,谢淑,等.含GDNF基因的慢病毒载体的构建和其在人胚胎神经干细胞中的表达[J].生物工程学报,2008,24(2): 2061-2067.[9] Wen GM, Li HW, Xiao QZ, et al. Zhongguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 2003;19(2):157-162.温冠媚,李浩威,肖庆忠,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞想造血细胞分化潜能的实验研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2003,19(2):157-162.[10] Van Damme A, Vanden Driessche T, Collen D, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells as targets for gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther. 2002;2(2):195-209.[11] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, et al. Adult rat and human bonemarrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370.[12] Zhong C, Zhong CJ, Luo YM, et al. Zhonghua Shenjing Yixue Zazhi. 2004;3(2):89-92.钟池,钟春玖,罗玉敏,等.骨髓基质细胞静脉移植治疗大鼠短暂性局灶性脑缺血[J].中华神经医学杂志,2004,3(2):89-92.[13] Gill SS, Patel NK, Hotton GR, et al. Direct brain infusion of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in Parkinson disease. Nat Med. 2003;9(5):589-595.[14] Mueller SM, Glowacki J. Age-related decline in the osteogenic potential of human bone marrow cells cultured in three-dimensional collagen sponges. J Cell Biochem. 2001; 82(4):583-590.[15] Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y, et al. Intravenous administration of human umbilical cod blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rat. Stroke. 2001;32(11):2682-2688.[16] Wexler SA, Donaldson C, Denning-Kendall P, et al. Adult bone marrow is a rich source of human mesenchymal ‘stem’ cells but umbilical cord and mobilized adult blood are not. Br J Haematol. 2003;121(2):368-374.[17] Rogers I, Casper RF. Umbilical cord blood stem cells. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2004;18(6):893-908.[18] Lin LF, Doherty DH, Lile JD, et al. GDNF: a glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Science. 1993;260(5111):1130-1132.[19] Can A, Karahusevinoglu S. Concise review: human umbilical cord stroma with regard to the source of fetus-derived stem cells. Stem Cells. 2007;25(11):2886-2895.[20] Kawasaki-Oyama RS, Braile DM, Caldas HC, et al. Blood mesemchymal stem cell culture from the umbilical cord with and without Ficoll-Paque density gradient method. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovsc. 2008;23(1):29-34. |